Transformers documentation
ConvNeXT
ConvNeXT
Overview
ConvNeXT モデルは、A ConvNet for the 2020s で Zhuang Liu、Hanzi Mao、Chao-Yuan Wu、Christoph Feichtenhofer、Trevor Darrell、Saining Xie によって提案されました。 ConvNeXT は、ビジョン トランスフォーマーの設計からインスピレーションを得た純粋な畳み込みモデル (ConvNet) であり、ビジョン トランスフォーマーよりも優れたパフォーマンスを発揮すると主張しています。
論文の要約は次のとおりです。
視覚認識の「狂騒の 20 年代」は、最先端の画像分類モデルとして ConvNet にすぐに取って代わられた Vision Transformers (ViT) の導入から始まりました。 一方、バニラ ViT は、オブジェクト検出やセマンティック セグメンテーションなどの一般的なコンピューター ビジョン タスクに適用すると困難に直面します。階層型トランスフォーマーです (Swin Transformers など) は、いくつかの ConvNet の以前の機能を再導入し、Transformers を汎用ビジョン バックボーンとして実用的に可能にし、幅広い環境で顕著なパフォーマンスを実証しました。 さまざまな視覚タスク。ただし、このようなハイブリッド アプローチの有効性は、依然として、固有の誘導性ではなく、トランスフォーマーの本質的な優位性によるところが大きいと考えられています。 畳み込みのバイアス。この作業では、設計空間を再検討し、純粋な ConvNet が達成できる限界をテストします。標準 ResNet を設計に向けて徐々に「最新化」します。 ビジョン Transformer の概要を確認し、途中でパフォーマンスの違いに寄与するいくつかの重要なコンポーネントを発見します。この調査の結果は、純粋な ConvNet モデルのファミリーです。 ConvNextと呼ばれます。 ConvNeXts は完全に標準の ConvNet モジュールから構築されており、精度と拡張性の点で Transformers と有利に競合し、87.8% の ImageNet トップ 1 精度を達成しています。 標準 ConvNet のシンプルさと効率を維持しながら、COCO 検出と ADE20K セグメンテーションでは Swin Transformers よりも優れたパフォーマンスを発揮します。
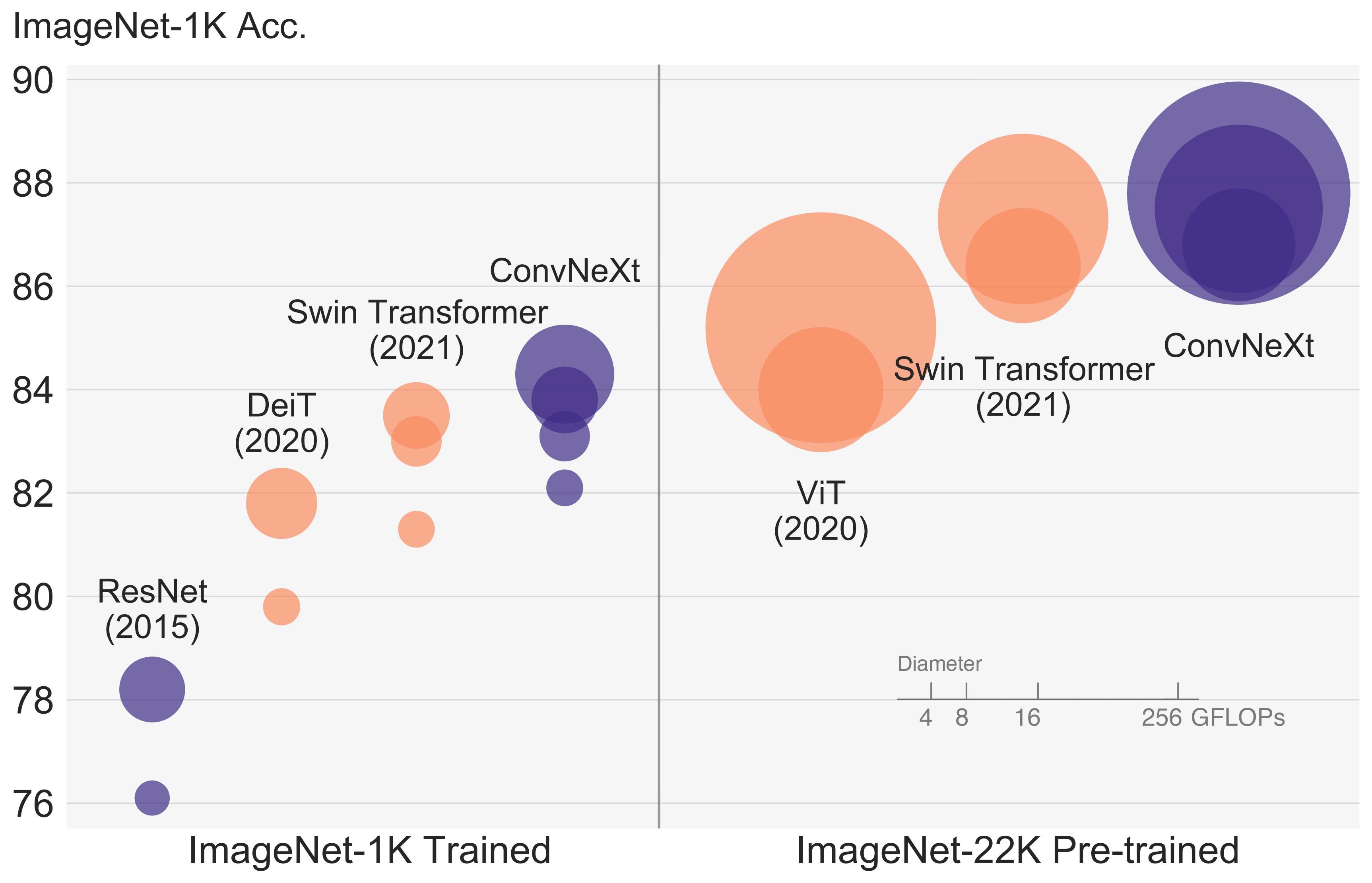 ConvNeXT アーキテクチャ。 元の論文から抜粋。
ConvNeXT アーキテクチャ。 元の論文から抜粋。 このモデルは、nielsr によって提供されました。 TensorFlow バージョンのモデルは ariG23498 によって提供されました。 gante、および sayakpaul (同等の貢献)。元のコードは こちら にあります。
Resources
ConvNeXT の使用を開始するのに役立つ公式 Hugging Face およびコミュニティ (🌎 で示される) リソースのリスト。
- ConvNextForImageClassification は、この サンプル スクリプト および ノートブック。
- 参照: 画像分類タスク ガイド
ここに含めるリソースの送信に興味がある場合は、お気軽にプル リクエストを開いてください。審査させていただきます。リソースは、既存のリソースを複製するのではなく、何か新しいものを示すことが理想的です。
ConvNextConfig
class transformers.ConvNextConfig
< source >( num_channels = 3 patch_size = 4 num_stages = 4 hidden_sizes = None depths = None hidden_act = 'gelu' initializer_range = 0.02 layer_norm_eps = 1e-12 layer_scale_init_value = 1e-06 drop_path_rate = 0.0 image_size = 224 out_features = None out_indices = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- num_channels (
int, optional, defaults to 3) — The number of input channels. - patch_size (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — Patch size to use in the patch embedding layer. - num_stages (
int, optional, defaults to 4) — The number of stages in the model. - hidden_sizes (
list[int], optional, defaults to [96, 192, 384, 768]) — Dimensionality (hidden size) at each stage. - depths (
list[int], optional, defaults to [3, 3, 9, 3]) — Depth (number of blocks) for each stage. - hidden_act (
strorfunction, optional, defaults to"gelu") — The non-linear activation function (function or string) in each block. If string,"gelu","relu","selu"and"gelu_new"are supported. - initializer_range (
float, optional, defaults to 0.02) — The standard deviation of the truncated_normal_initializer for initializing all weight matrices. - layer_norm_eps (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-12) — The epsilon used by the layer normalization layers. - layer_scale_init_value (
float, optional, defaults to 1e-6) — The initial value for the layer scale. - drop_path_rate (
float, optional, defaults to 0.0) — The drop rate for stochastic depth. - out_features (
list[str], optional) — If used as backbone, list of features to output. Can be any of"stem","stage1","stage2", etc. (depending on how many stages the model has). If unset andout_indicesis set, will default to the corresponding stages. If unset andout_indicesis unset, will default to the last stage. Must be in the same order as defined in thestage_namesattribute. - out_indices (
list[int], optional) — If used as backbone, list of indices of features to output. Can be any of 0, 1, 2, etc. (depending on how many stages the model has). If unset andout_featuresis set, will default to the corresponding stages. If unset andout_featuresis unset, will default to the last stage. Must be in the same order as defined in thestage_namesattribute.
This is the configuration class to store the configuration of a ConvNextModel. It is used to instantiate an ConvNeXT model according to the specified arguments, defining the model architecture. Instantiating a configuration with the defaults will yield a similar configuration to that of the ConvNeXT facebook/convnext-tiny-224 architecture.
Configuration objects inherit from PreTrainedConfig and can be used to control the model outputs. Read the documentation from PreTrainedConfig for more information.
Example:
>>> from transformers import ConvNextConfig, ConvNextModel
>>> # Initializing a ConvNext convnext-tiny-224 style configuration
>>> configuration = ConvNextConfig()
>>> # Initializing a model (with random weights) from the convnext-tiny-224 style configuration
>>> model = ConvNextModel(configuration)
>>> # Accessing the model configuration
>>> configuration = model.configConvNextImageProcessor
class transformers.ConvNextImageProcessor
< source >( do_resize: bool = True size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None crop_pct: typing.Optional[float] = None resample: Resampling = <Resampling.BILINEAR: 2> do_rescale: bool = True rescale_factor: typing.Union[int, float] = 0.00392156862745098 do_normalize: bool = True image_mean: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None **kwargs )
Parameters
- do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Controls whether to resize the image’s (height, width) dimensions to the specifiedsize. Can be overridden bydo_resizein thepreprocessmethod. - size (
dict[str, int]optional, defaults to{"shortest_edge" -- 384}): Resolution of the output image afterresizeis applied. Ifsize["shortest_edge"]>= 384, the image is resized to(size["shortest_edge"], size["shortest_edge"]). Otherwise, the smaller edge of the image will be matched toint(size["shortest_edge"]/crop_pct), after which the image is cropped to(size["shortest_edge"], size["shortest_edge"]). Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. Can be overridden bysizein thepreprocessmethod. - crop_pct (
floatoptional, defaults to 224 / 256) — Percentage of the image to crop. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeisTrueand size < 384. Can be overridden bycrop_pctin thepreprocessmethod. - resample (
PILImageResampling, optional, defaults toResampling.BILINEAR) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. Can be overridden byresamplein thepreprocessmethod. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to rescale the image by the specified scalerescale_factor. Can be overridden bydo_rescalein thepreprocessmethod. - rescale_factor (
intorfloat, optional, defaults to1/255) — Scale factor to use if rescaling the image. Can be overridden byrescale_factorin thepreprocessmethod. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toTrue) — Whether to normalize the image. Can be overridden by thedo_normalizeparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - image_mean (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_MEAN) — Mean to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_meanparameter in thepreprocessmethod. - image_std (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults toIMAGENET_STANDARD_STD) — Standard deviation to use if normalizing the image. This is a float or list of floats the length of the number of channels in the image. Can be overridden by theimage_stdparameter in thepreprocessmethod.
Constructs a ConvNeXT image processor.
preprocess
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']] do_resize: typing.Optional[bool] = None size: typing.Optional[dict[str, int]] = None crop_pct: typing.Optional[float] = None resample: typing.Optional[PIL.Image.Resampling] = None do_rescale: typing.Optional[bool] = None rescale_factor: typing.Optional[float] = None do_normalize: typing.Optional[bool] = None image_mean: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None image_std: typing.Union[float, list[float], NoneType] = None return_tensors: typing.Union[str, transformers.utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType] = None data_format: ChannelDimension = <ChannelDimension.FIRST: 'channels_first'> input_data_format: typing.Union[str, transformers.image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType] = None )
Parameters
- images (
ImageInput) — Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False. - do_resize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_resize) — Whether to resize the image. - size (
dict[str, int], optional, defaults toself.size) — Size of the output image afterresizehas been applied. Ifsize["shortest_edge"]>= 384, the image is resized to(size["shortest_edge"], size["shortest_edge"]). Otherwise, the smaller edge of the image will be matched toint(size["shortest_edge"]/ crop_pct), after which the image is cropped to(size["shortest_edge"], size["shortest_edge"]). Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - crop_pct (
float, optional, defaults toself.crop_pct) — Percentage of the image to crop if size < 384. - resample (
int, optional, defaults toself.resample) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. This can be one ofPILImageResampling, filters. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_rescale (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_rescale) — Whether to rescale the image values between [0 - 1]. - rescale_factor (
float, optional, defaults toself.rescale_factor) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_normalize (
bool, optional, defaults toself.do_normalize) — Whether to normalize the image. - image_mean (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults toself.image_mean) — Image mean. - image_std (
floatorlist[float], optional, defaults toself.image_std) — Image standard deviation. - return_tensors (
strorTensorType, optional) — The type of tensors to return. Can be one of:- Unset: Return a list of
np.ndarray. TensorType.PYTORCHor'pt': Return a batch of typetorch.Tensor.TensorType.NUMPYor'np': Return a batch of typenp.ndarray.
- Unset: Return a list of
- data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional, defaults toChannelDimension.FIRST) — The channel dimension format for the output image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format.- Unset: Use the channel dimension format of the input image.
- input_data_format (
ChannelDimensionorstr, optional) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
Preprocess an image or batch of images.
ConvNextImageProcessorFast
class transformers.ConvNextImageProcessorFast
< source >( **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.models.convnext.image_processing_convnext.ConvNextImageProcessorKwargs] )
Constructs a fast Convnext image processor.
preprocess
< source >( images: typing.Union[ForwardRef('PIL.Image.Image'), numpy.ndarray, ForwardRef('torch.Tensor'), list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']] **kwargs: typing_extensions.Unpack[transformers.models.convnext.image_processing_convnext.ConvNextImageProcessorKwargs] ) → <class 'transformers.image_processing_base.BatchFeature'>
Parameters
- images (
Union[PIL.Image.Image, numpy.ndarray, torch.Tensor, list['PIL.Image.Image'], list[numpy.ndarray], list['torch.Tensor']]) — Image to preprocess. Expects a single or batch of images with pixel values ranging from 0 to 255. If passing in images with pixel values between 0 and 1, setdo_rescale=False. - do_convert_rgb (
bool, optional) — Whether to convert the image to RGB. - do_resize (
bool, optional) — Whether to resize the image. - size (
Annotated[Union[int, list[int], tuple[int, ...], dict[str, int], NoneType], None]) — Describes the maximum input dimensions to the model. - crop_size (
Annotated[Union[int, list[int], tuple[int, ...], dict[str, int], NoneType], None]) — Size of the output image after applyingcenter_crop. - resample (
Annotated[Union[PILImageResampling, int, NoneType], None]) — Resampling filter to use if resizing the image. This can be one of the enumPILImageResampling. Only has an effect ifdo_resizeis set toTrue. - do_rescale (
bool, optional) — Whether to rescale the image. - rescale_factor (
float, optional) — Rescale factor to rescale the image by ifdo_rescaleis set toTrue. - do_normalize (
bool, optional) — Whether to normalize the image. - image_mean (
Union[float, list[float], tuple[float, ...], NoneType]) — Image mean to use for normalization. Only has an effect ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue. - image_std (
Union[float, list[float], tuple[float, ...], NoneType]) — Image standard deviation to use for normalization. Only has an effect ifdo_normalizeis set toTrue. - do_pad (
bool, optional) — Whether to pad the image. Padding is done either to the largest size in the batch or to a fixed square size per image. The exact padding strategy depends on the model. - pad_size (
Annotated[Union[int, list[int], tuple[int, ...], dict[str, int], NoneType], None]) — The size in{"height": int, "width" int}to pad the images to. Must be larger than any image size provided for preprocessing. Ifpad_sizeis not provided, images will be padded to the largest height and width in the batch. Applied only whendo_pad=True. - do_center_crop (
bool, optional) — Whether to center crop the image. - data_format (
Union[str, ~image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType]) — OnlyChannelDimension.FIRSTis supported. Added for compatibility with slow processors. - input_data_format (
Union[str, ~image_utils.ChannelDimension, NoneType]) — The channel dimension format for the input image. If unset, the channel dimension format is inferred from the input image. Can be one of:"channels_first"orChannelDimension.FIRST: image in (num_channels, height, width) format."channels_last"orChannelDimension.LAST: image in (height, width, num_channels) format."none"orChannelDimension.NONE: image in (height, width) format.
- device (
Annotated[str, None], optional) — The device to process the images on. If unset, the device is inferred from the input images. - return_tensors (
Annotated[Union[str, ~utils.generic.TensorType, NoneType], None]) — Returns stacked tensors if set to `pt, otherwise returns a list of tensors. - disable_grouping (
bool, optional) — Whether to disable grouping of images by size to process them individually and not in batches. If None, will be set to True if the images are on CPU, and False otherwise. This choice is based on empirical observations, as detailed here: https://github.com/huggingface/transformers/pull/38157 - crop_pct (
float, optional) — Percentage of the image to crop. Only has an effect if size < 384. Can be overridden bycrop_pctin thepreprocessmethod.
Returns
<class 'transformers.image_processing_base.BatchFeature'>
- data (
dict) — Dictionary of lists/arrays/tensors returned by the call method (‘pixel_values’, etc.). - tensor_type (
Union[None, str, TensorType], optional) — You can give a tensor_type here to convert the lists of integers in PyTorch/Numpy Tensors at initialization.
ConvNextModel
class transformers.ConvNextModel
< source >( config )
Parameters
- config (ConvNextModel) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
The bare Convnext Model outputting raw hidden-states without any specific head on top.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None output_hidden_states: typing.Optional[bool] = None ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size), optional) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using ConvNextImageProcessor. SeeConvNextImageProcessor.__call__()for details (processor_classuses ConvNextImageProcessor for processing images). - output_hidden_states (
bool, optional) — Whether or not to return the hidden states of all layers. Seehidden_statesunder returned tensors for more detail.
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.BaseModelOutputWithPoolingAndNoAttention or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (ConvNextConfig) and inputs.
-
last_hidden_state (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width)) — Sequence of hidden-states at the output of the last layer of the model. -
pooler_output (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, hidden_size)) — Last layer hidden-state after a pooling operation on the spatial dimensions. -
hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each layer) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width).Hidden-states of the model at the output of each layer plus the optional initial embedding outputs.
The ConvNextModel forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
ConvNextForImageClassification
class transformers.ConvNextForImageClassification
< source >( config )
Parameters
- config (ConvNextForImageClassification) — Model configuration class with all the parameters of the model. Initializing with a config file does not load the weights associated with the model, only the configuration. Check out the from_pretrained() method to load the model weights.
ConvNext Model with an image classification head on top (a linear layer on top of the pooled features), e.g. for ImageNet.
This model inherits from PreTrainedModel. Check the superclass documentation for the generic methods the library implements for all its model (such as downloading or saving, resizing the input embeddings, pruning heads etc.)
This model is also a PyTorch torch.nn.Module subclass. Use it as a regular PyTorch Module and refer to the PyTorch documentation for all matter related to general usage and behavior.
forward
< source >( pixel_values: typing.Optional[torch.FloatTensor] = None labels: typing.Optional[torch.LongTensor] = None **kwargs ) → transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
Parameters
- pixel_values (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, num_channels, image_size, image_size), optional) — The tensors corresponding to the input images. Pixel values can be obtained using ConvNextImageProcessor. SeeConvNextImageProcessor.__call__()for details (processor_classuses ConvNextImageProcessor for processing images). - labels (
torch.LongTensorof shape(batch_size,), optional) — Labels for computing the image classification/regression loss. Indices should be in[0, ..., config.num_labels - 1]. Ifconfig.num_labels == 1a regression loss is computed (Mean-Square loss), Ifconfig.num_labels > 1a classification loss is computed (Cross-Entropy).
Returns
transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or tuple(torch.FloatTensor)
A transformers.modeling_outputs.ImageClassifierOutputWithNoAttention or a tuple of
torch.FloatTensor (if return_dict=False is passed or when config.return_dict=False) comprising various
elements depending on the configuration (ConvNextConfig) and inputs.
- loss (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(1,), optional, returned whenlabelsis provided) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) loss. - logits (
torch.FloatTensorof shape(batch_size, config.num_labels)) — Classification (or regression if config.num_labels==1) scores (before SoftMax). - hidden_states (
tuple(torch.FloatTensor), optional, returned whenoutput_hidden_states=Trueis passed or whenconfig.output_hidden_states=True) — Tuple oftorch.FloatTensor(one for the output of the embeddings, if the model has an embedding layer, + one for the output of each stage) of shape(batch_size, num_channels, height, width). Hidden-states (also called feature maps) of the model at the output of each stage.
The ConvNextForImageClassification forward method, overrides the __call__ special method.
Although the recipe for forward pass needs to be defined within this function, one should call the
Moduleinstance afterwards instead of this since the former takes care of running the pre and post processing steps while the latter silently ignores them.
Example:
>>> from transformers import AutoImageProcessor, ConvNextForImageClassification
>>> import torch
>>> from datasets import load_dataset
>>> dataset = load_dataset("huggingface/cats-image")
>>> image = dataset["test"]["image"][0]
>>> image_processor = AutoImageProcessor.from_pretrained("facebook/convnext-tiny-224")
>>> model = ConvNextForImageClassification.from_pretrained("facebook/convnext-tiny-224")
>>> inputs = image_processor(image, return_tensors="pt")
>>> with torch.no_grad():
... logits = model(**inputs).logits
>>> # model predicts one of the 1000 ImageNet classes
>>> predicted_label = logits.argmax(-1).item()
>>> print(model.config.id2label[predicted_label])
...